It goes without saying that nobody can do without energy. Being one of the decisive factors, the availability of energy resources is crucial for economic growth and ultimately for the well-being of individuals. Numerous forecasts share similar core findings that there exists a fundamental need to expand and diversify supplies of energy, improve efficiency, and eliminate environmental risks. According to ExxonMobil’s report „2012 The Outlook for Energy: A View to 2040“, the global energy demand will be about 30% higher in 2040 compared to 2010, and the quantity of the population will go up to nearly 9 billion people from about 7 billion today.
To successfully tackle the existing challenges the energy sector requires a wide array of innovations. Mobility is one of the fastest-growing and most exciting trends today. The mass adoption of smartphones and tablets is creating new opportunities for energy companies to boost efficiency and profits.
Here one should bear in mind that the energy industry encompasses a variety of subindustries, including the petroleum industry, the gas industry, the electrical power industry, the coal industry, the nuclear power industry, the renewable energy industry, etc.
Early adopters of mobile technologies have quickly recognized the value of enabling their workforce with fast, mobile data access via an easy-to-use interface. In addition to internal purposes, mobile devices are being used by energy businesses also through application development as a way to connect with customers. Therefore, mobile apps from such companies can be roughly categorized into two main groups: apps for in-house use and apps for consumers.
In-house apps
Naturally, any business wants to keep expenditures down and profits high. Industry-specific in-house apps can range from monitoring and diagnostic tools to business intelligence collection resources. Mobile applications can be specifically designed for energy industry field workers, including drilling crews, maintenance technicians, mechanics, supervisors, instrumentation techs, safety managers, and others. Such apps for mobile devices, primarily for tablets, like the iPad, can allow inventory managing, diagnostic information collection, data acquisition, remote telemetry control, and other support functions.
The major benefits of mobile apps for energy businesses may be the following:
- Easy and quick access to information and key performance indicators;
- Standardization, simplification, and automation of operations and business processes;
- Easy flow of information;
- Increased quality in the level of services;
- Greater productivity and improved operational effectiveness;
- Higher integration of fragmented and delocalized processes;
- Automatic synchronization with corporate systems;
- Improved data exchange;
- Employee professional growth;
- Higher quality of real-time measurements;
- The ability to zoom in from a global map to a specific industrial object or section.
Mobile apps imply a step-by-step approach to ensure that each job is done in accordance with the company’s guidelines, safely and correctly. In addition to the increase in individual productivity and performance, mobile apps provide value to the entire organization through the timely collection and delivery of accurate field information to the corporate office. Furthermore, field workers instead of multiple software systems can use a single, field-specific application to seamlessly interact with corporate systems.
As early as 2011 General Electric reported about distributing 2,000 iPads internally and developing a series of applications both for its employees and customers. One mobile app allows employees to approve purchase orders on the go, while another one allows utility service personnel to monitor the company’s transformers in the field.
Apps for consumers
Energy companies in their relationship with customers can emphasize energy efficiency rather than simply focus on price and tariffs. With the help of mobile applications, consumers can cut wasteful energy consumption and hence their expenses.
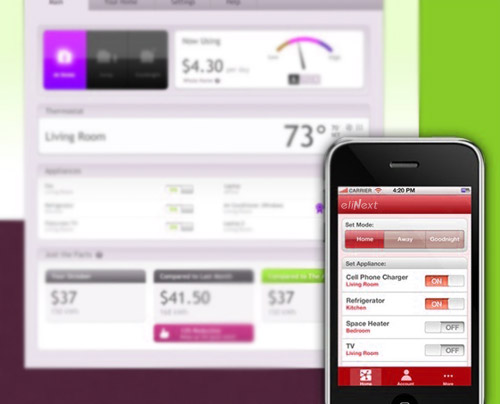
Certain research studies have proved that homeowners who are able to check how much electricity they are using in real-time save on the average more than 10% of energy almost immediately by turning off unnecessary lights and appliances. Improving consumers‘ access to data about how they use energy in their homes will allow them to use mobile devices to calculate potential savings on their energy bills, increase energy literacy, and reduce energy consumption.
Consumers can, for example, determine personalized lighting scenarios, control room temperature settings, and the heating system in order to ensure that the home isn’t utilizing unnecessary heating while unoccupied. A mobile app in this way turns a smartphone, like the iPhone or Android, or a tablet, like the iPad, into the remote control for the home energy system. This also provides a unique way for homeowners to get more comfort and enjoyment from their homes, devices, and appliances.
In general, consumers may benefit from the following features of energy companies‘ apps:
- Improved efficiency, transparency, and visualization of energy consumption;
- Detailed energy usage information per device in the home;
- Automation and control of electronic home devices;
- Integration with social platforms;
- Updates on tariffs and prices;
- Hints and tips on saving energy.
Mobile applications thus raise consumers‘ awareness and increase the growing market of home automation customers.
Conclusion
In combination with the unique capabilities of mobile devices themselves, custom mobile apps allow businesses to translate their creative and innovative ideas into new opportunities. Tech-savvy energy business leaders are using iPads and Android tablets to arm mobile workers, improve internal efficiencies, reach out to new customers, and build customer loyalty.
Industries and Technology Areas:
Industries: energy industry, petroleum industry, gas industry, electrical power industry, coal industry, renewable energy industry
Technology Areas: mobile application development, software development, iOS, iPhone, iPad, Android, BlackBerry, Windows Phone, tablet