5G promises to provide essential levels of connectivity to enable a new health ecosystem, one that can meet patient and provider needs accurately, efficiently, conveniently, cost-effectively, and at a substantial scale. However to realize the full potential of 5G networks in healthcare settings, network security, and data privacy are paramount.
The transformation and improvement of critical components of healthcare infrastructure are closely connected with the usage of 5G technology. The spread of 5G in healthcare is especially important in the light of coronavirus pandemics, which causes unprecedented stress on health systems worldwide.
5G enables a not-before-seen level of connectivity. It, in turn, is able to create a new healthcare ecosystem. The one with more efficiency, convenience, and cost-effectiveness in communication between patients and physicians. Those are just a few of the upsides of just one of the applications of the technology.
Being realized at a large scale, 5G networks create an environment that allows healthcare providers to erase any problems caused by slow network connections. Therefore, such improvements create a high quality of daily patient care and create better outcomes in the long run.
In this blog post, we’ll talk about the current 5G spread around the world, the most obvious applications of the technology in healthcare to the date: improvement of telemedicine, . We will also give you real-life examples of improvement.
In our later publications, we’ll dive deeper into the research of more complex applications of 5G networks in healthcare, such as robotics, remote medical procedures, and others.
Stay tuned, and now let’s dive into 5G in more or less healthcare 101.
5G: Future, or Reality in Modern Healthcare
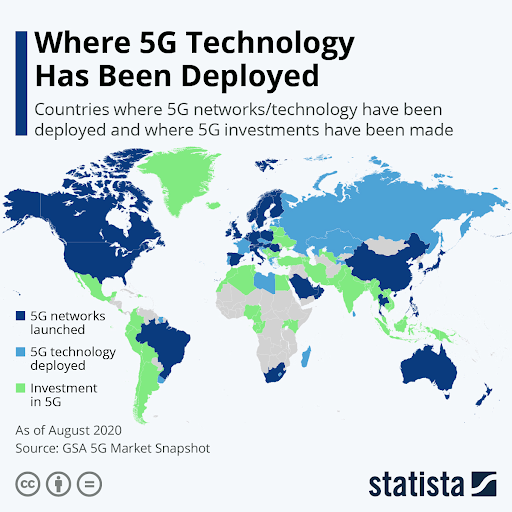
5G has been in big talks and wide deployment phase since 2018. If we’re speaking about commercial services, by September 2020, the technology had been deployed in 18 (EU-27 plus the UK) countries.
5GObservatory also claims that it is utilized by all major US, Australian, South Korean cellular providers. All their major players have launched 5G services around their countries.
Statista research shows that by 2025, almost 60 percent of mobile subscriptions in South Korea (5g pioneers) are expected to be for 5G networks. Then it comes to 5G speed, the country is currently being beaten by Saudi Arabia, according to Open Signal.
Overall, the world 5G launch map looks the following way:
Source: statista.com
But that is commercial use. What applications should 5G have in healthcare specifically?
To begin with, in a hospital ward in Wuhan – at that point, an epicenter for global COVID-19 outbreak – 12 robots were operating. They were taking temperatures of patients, delivering food to them, disinfected the room.
5G provided enough speed for healthcare workers to distance themselves from patients and get a safer ward to work from.
PwC report on 5G in healthcare highlights the following areas on 5G features bring value: telehealth, remote surgeries, transferring medical files of large sizes, tracking patients movements, real-time monitoring of wearable devices, delivering treatment information, delivering support to patients.
In the next section, we’ll say a few words about the practical use of 5G in modern healthcare.
Most Obvious Ways of how 5G Helps in Healthcare
Fast Transmitting of Large Imaging Files
That same PwC report suggests that 5G is capable of achieving speeds that are more or less 100 times faster than 4G speed.
Source: pixabay.com
There are plenty of areas in medicine where large files are generated in big numbers. That is especially true for MRI and other image machines files that are often sent to doctors review. With the low speeds of the Internet, the transmission takes a longer time, and there are many errors where images aren’t sent properly.
This affects the treatment, and some delays in it might be critical – after all, we’re dealing with people’s health.
When we have a much higher (100 times higher) network speed, this creates a whole new better channel for transmitting these big data files of healthcare images. That makes access to healthcare and the quality of that care much improved.
AT&T reported that sharing large PET scans, MRIs and other digital medical images created problems at Austin Cancer Center. With the help of a mobile provider, Austin Cancer Center’s technology team was able to deliver improved network performance at a lower cost.
Jason Lindgren, CIO of the center, commented on that:
“To get that much data from one side of the town to another, you’ve got to have the network performance to handle it. Without Network on Demand, I don’t think we could have accomplished improved performance.”
Instead of hours spent on images transmitting, they’ve done it in a matter of minutes when 5G stepped on the stage.
Expanding the Use of Telemedicine
The global telemedicine market size is projected to reach 185.66 billion by 2026, exhibiting a CAGR of 23.5% during the forecast period.
The coronavirus pandemic contributed to rapid advancements in technologies that transform the healthcare industry.
This, as a result, has bought some significant changes in telemedicine, especially regarding its accessibility and availability.
COVID-19 can affect the global economy in three main ways: by directly affecting production and demand, by creating supply chain and market disruption, and by its financial impact on firms and financial markets.
The demand for telemedicine grew exponentially. Any telecom technologies were experiencing a boom, just try to remember how Zoom stock market grew back at the beginning of the global spread of COVID-19.
Source: bartonassociates.com
Telemedicine requires a network that can support real-time high-quality video, which often means wired networks.
Utilizing 5G, healthcare facilities and professionals enable mobile networks to take care of appointments. That way patients get timely visits, and therefore, care, and often have access to communicating with specialists that, hence the technology was unavailable, wouldn’t be possible.
5G also allows doctors and other medical workers to collaborate more efficiently.
Artificial Intelligence, Augmented and Virtual Reality and 5G
AI is becoming a sufficient part of the healthcare ecosystem. Artificial intelligence is able to help with diagnoses, choose the best possible treatment plans out of several options, enable to predict possible outcomes of the surgery or other medical procedures.
Obviously, large amounts of data needed to be processed for AI to fully enter the game. The data for real-time rapid learning requires reliable and high-bandwidth networks.
Providers often need to access data from their mobile devices. By enabling Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning through 5G networks, healthcare systems can improve the quality of care and patient experience, reducing the cost of care.
5G networks enable providers to provide more personalized and preventive care
Contact us to learn more about how your specific business can embrace next-generation technologies with the help of Elinext specialists.
Talking about augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and spatial computing, the most famous case study about 5G and connections with these technologies is AT&T and VITAS Healthcare.
The goal of their collaboration is to reduce pain and anxiety for terminally ill patients in hospice by providing calming, distracting content via 5G-enabled AR and VR.
AT&T also claims that live streams of VR cancer surgeries placed online and broadcasted with the help of 5G are crazily effective for future doctors and gain more popularity than rock concerts of indie bands.
Source: att.com
Summary
Erasing all the other aspects, 5G is all about increasing connectivity speed. The new capabilities open a wide usage of unconventional tech in never-before-seen healthcare infrastructure. AI and ML, AR and VR, hard diagnostics, and dozens of other factors come into play.
5G provides essential levels of connectivity to enable a new health ecosystem, one that can meet patient and provider needs accurately, efficiently, conveniently, and cost-effectively.