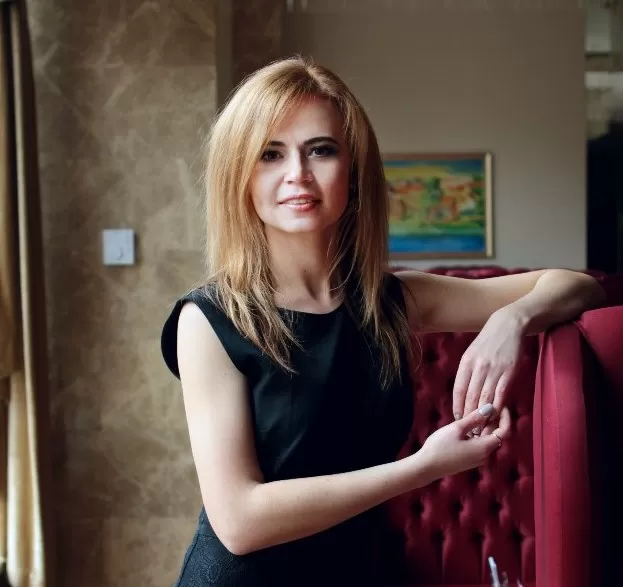
According to the latest Spyglass Study (Trends in remote patient monitoring) that was based on the telephone interviews over 100 health IT thought leaders, the majority (88%) of U.S. healthcare providers surveyed have invested or are considering new investments in RPM solutions to provide quality and cost-effective treatment for chronic disease management.
Meanwhile IDTechEX Report “Technologies for Diabetes Management 2019-2029” forecasts a vast market expansion of technologies for continuous patient monitoring to manage high-risk patients with chronic conditions, including diabetes: the biomedical sensors market will score $43 billion, and revenue from electronic skin patches will reach more than $20 billion by 2029.
In addition to this, Grand View Research recently predicted that the global digital diabetes management market will run to $26,4 billion by 2026, registering a CAGR of 19,4% over the forecast period.
WHY IT MATTERS
The above mentioned statistics just illustrate the key factors that influence new trends in the 2020 health ecosystem and digital innovations in diabetes treatment:
- a growing geriatric population with unhealthy diets is increasingly suffering from diabetes more and more all over the world and requires patients’ self-involvement in the remote treatment of diabetes;
- focus on quality value-based care and home self-monitoring for patients with chronic diseases stimulates healthcare providers rise spending on connected health solutions;
- a wide range of innovations, devoted to remote monitoring, has been developed and is considered continue to grow in mHealth, telehealth, IoT, and artificial intelligence sectors.
WHAT ARE THE LEADING SOLUTIONS FOR DIGITAL DIABETES MANAGEMENT?
Let’s dive into the world of digital diabetes market and see what innovative healthcare solutions have already been developed and released by digital healthcare companies and which should appear in the near future to diminish the growing incidence of diabetes. Here you can see market split between the leading players in the digital diabetes market which manufacture devices and develop software and apps for diabetes management:
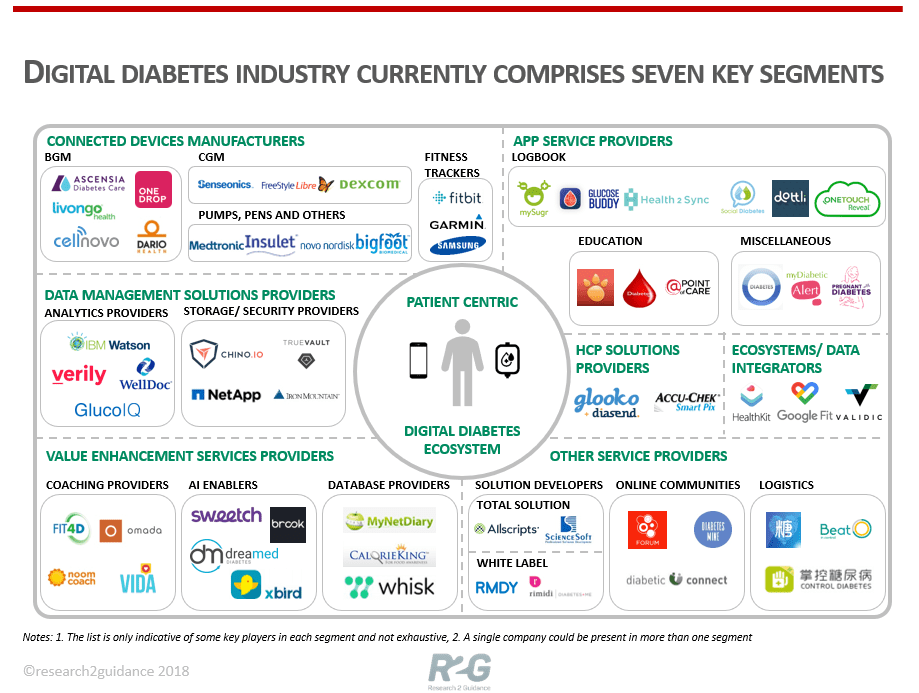
Source: research2guidence
DIABETES TRACKING DEVICES
The unprecedented growth of diabetes technology, including software, applications, and hardware, significantly improve the lifestyle and health of people with diabetes. Today, people with diabetes mellitus have the opportunity to receive in-home care instead of hospitalization thanks to connected healthcare systems.
However, diabetes is still difficult to monitor due to the transmission of big data and the accuracy of transmitted key indicators. There are three categories of remote diabetes monitoring devices that transmit data to clinicians and provide home healthcare: glucose and blood pressure monitoring sensors, insulin delivery devices, and hybrid closed-loop systems.
MONITORING DEVICES
Smart Blood Pressure Monitoring Devices change diabetes care, reduce the risk of heart failures due to high blood pressure and simplify personal healthcare management thanks to a combination of traditional devices and modern technologies that continuously monitor blood pressure, fulfill wireless data transfer and display personal results in mobile applications.
Glucose Monitoring Devices are glucose sensors that measure blood sugar, collect patient-generated health information (PGHD) and transmit data to medical devices. And due to mHealth, the number of RPM devices with integrated cellular connectivity will increase significantly in the near future.
We can split up glucose tracking sensors and non-invasive glucose monitoring devices for remote patient monitoring of patients in the following categories:
- Glucose Meters
Devices are used when people with diabetes perform self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) to check their health and measure the effects of their telehealth therapy, including diet, exercise, diabetes pills, and insulin control to prevent hypoglycemia.
State-of-the-art glucose sensors are combined with no-wipe technology to make finger lancet pricking procedures painless. Blood glucose device (BGD) can use Bluetooth or cellular networks to wirelessly transmit health data to the cloud, data-management software and mobile applications on a patient’s Smartphone, so doctors or patients have easy access to readings.
- Real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rtCGM)
The next-generation sensors for needleless remote patient monitoring are presented with special patches for measuring glucose levels in the intercellular fluid between cells and providing with active alarms about a dangerous condition. The tiny rtCGM sensor, embedded under the skin, constantly checks glucose levels and transmits data wirelessly to the receiver – a separate monitor or part of an insulin pump. And then the data can be uploaded to a diabetes management app or software to monitor diabetes trends.
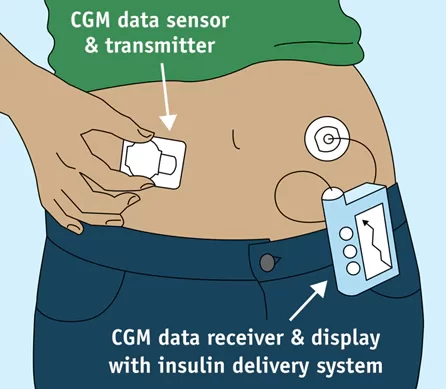
Source: U.S. Food and Drug Administration
- Intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring (isCGM) or Flash Glucose Monitoring
The isCGM system is another needle-free alternative to finger-stick tests that measures glucose concentration and transmits glucose data to a smartphone or wearable device for clinical use. It is very similar to rtCGM technology, but there are some differences. A flash glucose monitoring sensor is placed under the skin and measures the amount of glucose in the fluid of body cells. There is no alerts function here and isCGM requires the patient to scan the flash sensor to obtain the necessary data.
INSULIN DELIVERY
Insulin Delivery Devices are aimed to inject insulin as a vital treatment for patients with diabetes. It is not surprising that today there are many methods for delivering insulin. Let’s look at the more promising ones:
- Bluetooth connected Insulin Pens or Smart Pens
The latest generation of insulin pens combines aspects of injector pens, bolus calculators, Bluetooth technology, and smartphone apps. And even this innovative approach cannot guarantee an accurate imitation of the natural function of the pancreas, since it is easy for the patient to lose count on injections. In this regard, leading health IT providers are developing devices with automatic insulin injection or insulin pumps.
- Insulin Pump Technology
Insulin pumps are continuously delivering insulin devices that transfer insulin from a special reservoir to the infusion set needle inserted under the skin. Modern wearables are equipped with a bolus advisor to make accurate dose calculation based on blood glucose readings and carbohydrate content in the diet and are known as hybrid next-generation diabetes devices.
- Automated Insulin Delivery (AID)
Artificial Pancreas Systems (insulin pump + CGM) are designed to communicate with other compatible devices and serve to simultaneously deliver insulin and monitor blood glucose levels. Artificial pancreas device technology is seen as the future of CGM, which can imitate the natural function of the pancreas to control insulin in the body.
The only system called a hybrid closed loop system consists of a combination of an insulin pump and a continuous glucose monitoring device (CGM) and a blood glucose meter to double check received data. The system is based on a computer-controlled algorithm and provides communication between devices that continuously check blood pressure and glucose levels and automatically enter the correct dose of insulin, replacing the function of the pancreas.
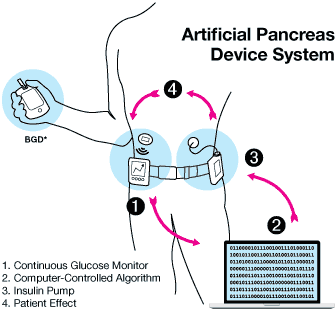
Source: U.S. Food and Drug Administration
FINISHING TOUCHES
There is no doubt that healthcare development companies will continue to look for new, effective ways to use implantable devices and non-invasive wireless sensors, as well as near-field communications (NFS) for chronic disease management. And healthcare leaders will continue to invest in providing remote patient monitoring, ultra-precise insulin delivery and the development of an artificial pancreas system similar to a natural organ in 2020.
In our article “Connected Devices for Diabetes Management and Monitoring” you can find alternative solutions and the selection of amazing wearable devices for diabetes self-control.
In the article “Software for Diabetes Control in 2021“ – find the latest trends in the diabetes management market.